The Gambia's tropical climate and abundant water resources—including the Gambia River and wetlands—provide excellent conditions for aquaculture. Fish serve as a vital local protein source, and aquaculture not only compensates for wild fisheries shortfalls but also boosts farmers' incomes, advancing food security and rural economic development.
This article focuses on the practical needs of Gambian aquaculture, sharing proven low-cost, easy-to-implement methods—from pond design to feed formulation, water quality management to disease prevention—to comprehensively help farmers boost fish growth rates and maximize farming profitability.
Understanding Fish Growth Patterns in The Gambia's Environment
Mainstream Aquaculture Species
Gambian farmers primarily cultivate highly adaptable, fast-growing species, including tilapia, catfish (especially leatherjaw catfish), and catfish. These species tolerate low temperatures and low oxygen levels, making them well-suited for local pond conditions. With strong market demand, they are optimal choices for boosting farmer incomes.
Key Environmental Factors Affecting Fish Growth
- Water Temperature Regulation: Gambia's annual average temperature ranges between 25-30°C, closely matching the optimal growth range of 25-32°C for tilapia and catfish. However, during extreme heat periods, timely cooling measures such as shade netting and recirculating water systems are essential to prevent excessive temperatures from inhibiting fish growth.
- Water Quality Management Essentials: Dissolved oxygen, pH levels, and ammonia nitrogen content are core indicators for water quality monitoring. Adequate dissolved oxygen ensures efficient fish metabolism, stable pH (6.5–8.5) maintains water acid-base balance, and strict control of ammonia nitrogen concentration (≤0.2 mg/L) effectively prevents reduced feeding capacity and health damage in fish.
- Feed Supply Challenges: The consistent and stable supply of high-quality feed represents a critical constraint for Gambian fish farming development. Establishing localized feed production systems or optimizing supply chains is vital for meeting fish nutritional needs and enhancing farming profitability.
Core Challenges Facing Local Farmers
During the development of Gambia's aquaculture industry, farmers commonly encounter three major core challenges: First, persistently high prices for quality feed coupled with market supply gaps directly inflate farming costs; Second, water scarcity during the dry season leads to deteriorating water quality, severely threatening fish survival environments.
Third, farmers lack technical expertise in critical management areas, including controlling appropriate stocking densities and early detection and prevention of fish diseases. These intertwined challenges result in slow fish growth and significantly reduced survival rates.
Optimizing Pond Design and Management
Scientific Site Selection
Pond locations must meet three critical criteria: prioritize areas near stable water sources (e.g., rivers, wells) to ensure uninterrupted water replenishment during dry seasons; soil types should be loam or clay to minimize water seepage losses; terrain should be moderately elevated with effective drainage systems to prevent floodwater backflow and pond inundation during rainy seasons.
Pond Pre-treatment
- Lime Amendment: 1-2 weeks before stocking, uniformly spread quicklime at 50-100 kg per mu to precisely adjust soil pH to 6.5-8.5. This eliminates latent pathogens and parasites, purifying the pond environment.
- Fertilization and Water Cultivation: Utilize abundant local organic resources such as cattle manure and chicken manure, applying 200-300 kg per mu to fertilize and cultivate the water. The decomposition of organic matter promotes massive reproduction of plankton, providing natural, high-quality feed for fry.
- Predator Removal: Conduct thorough pond cleaning before stocking, focusing on eliminating harmful species like snakes, frogs, and wild fish to prevent predation threats or competition for feed resources with cultured fish.
Key Daily Maintenance Points
- Aquatic Plant Management: Establish a regular manual removal system to promptly eliminate excessive aquatic weeds like duckweed and water hyacinth. This prevents overgrowth that blocks sunlight and depletes dissolved oxygen. Maintain an appropriate amount of aquatic plants to maximize their ecological role in water purification.
- Routine Inspection Monitoring: Implement weekly patrols to observe pond water quality changes (ideal water color is light green or yellowish-brown) and fish behavior (e.g., gasping at the surface, feeding activity), enabling swift identification and resolution of abnormalities.
- Periodic Dredging Operations: After each farming cycle, thoroughly remove a 10-15 cm layer of bottom sediment to effectively reduce accumulation of harmful substances like ammonia nitrogen and hydrogen sulfide, creating optimal conditions for the next cycle.
Water Quality Improvement
Core Water Quality Requirements
- Dissolved Oxygen: Must be consistently maintained above 5 mg/L. Concentrations below 3 mg/L cause fish to surface for air, halt growth, and may lead to mortality in severe cases.
- pH Level: Ideal range is 6.5–8.5. Water outside this range—whether excessively acidic or alkaline—damages fish gill tissue, disrupting respiration and metabolism.
- Water Temperature: Preventing drastic fluctuations is crucial. During hot seasons, effective cooling can be achieved by deepening water levels to 1.5–2 meters or installing shade structures.
Low-Cost Water Quality Maintenance Methods
- Natural Aeration: Plant aquatic vegetation like water hyacinth and elodea in ponds. These plants release oxygen through photosynthesis while absorbing harmful substances like ammonia nitrogen, achieving ecological purification.
- Artificial Aeration: For small-scale operations, use bucket-style agitation—stirring the water for 10 minutes twice daily (morning and evening). For large-scale farms with unstable power supply, solar aerators are recommended for energy efficiency and practicality.
- Scientific Water Exchange: During dry seasons, replace one-third of total pond water every 10–15 days. In rainy seasons, reduce frequency based on water quality while promptly draining surface pollutants.
Local Solutions for Smallholders
Leverage Gambia's abundant coconut shells and palm leaves to construct simple filtration devices installed at water inlets, effectively intercepting impurities and pathogens. Collect local clay to produce biochar, evenly distributing 50 kg per mu into ponds. This strongly adsorbs harmful substances in the water, significantly improving water quality.
Feed and Nutrition
Fundamental Feeding Principles
- Core Value of Premium Feed: Nutrients like protein, amino acids, and vitamins in feed are critical for fish growth. Using high-quality feed stabilizes the feed conversion ratio (FCR) between 1.5–2.0, meaning 1.5 kg of feed produces 1 kg of marketable fish, significantly boosting farming profitability.
- Precision Feeding Strategy: Adopt a scientific “small-quantity, multiple-feedings” approach with 2-3 daily feedings scheduled between 8-9 AM and 4-5 PM. Avoid midday feedings during hot seasons. Optimal single-feeding quantities allow fish to consume within 5-10 minutes, ensuring efficient feed utilization.
- Localized Feed Formulation: Leverage Gambia's abundant local raw materials to independently formulate feed, effectively reducing production costs. Recommended Classic Formula: Peanut cake 30% + Rice bran 25% + Soybean meal 20% + Corn flour 15% + Shrimp shell meal / Earthworm meal (or other fish meal substitutes) 10%. Mix ingredients to form palatable pellets or powdered feed.
- Feeding Management Essentials: Spread feed evenly along pond edges at a steady pace. Closely monitor fish feeding behavior, promptly remove uneaten feed to prevent spoilage, and avoid water quality degradation.
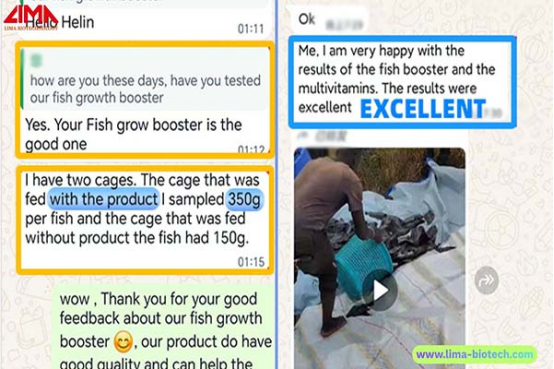
High-Efficiency Fish Growth Booster
Addressing Gambian aquaculture challenges, this fermented feed additive is specifically engineered for local conditions. It significantly boosts fish growth rates and stress resistance. Key advantages and application methods:
Core Advantages
- Strengthened Stress Resistance: Enhances fish tolerance to extreme conditions like Gambia's dry season heatwaves and drastic water quality fluctuations, significantly reducing stress-related mortality.
- Optimized Gut Ecology: Precisely regulates intestinal microflora balance, substantially improving feed conversion rates and addressing nutritional imbalances in local feed formulations.
- Fortified Immune Barrier: Deeply activates the fish's immune defense system, significantly reducing the likelihood of bacterial and parasitic infections, particularly suitable for high-density intensive farming models.
- Self-Cleaning System: Accelerates the degradation of organic pollutants in the water, strongly inhibits the accumulation of harmful substances such as ammonia nitrogen and nitrite, and significantly reduces the frequency of manual water changes.
- Protects Hepatobiliary Health: Establishes a protective system for fish livers, effectively preventing hepatobiliary disorders caused by feed spoilage or overfeeding.
- Precisely Controls Feed Efficiency Conversion: Through intelligent nutrient absorption regulation, minimizes feed wastage, achieves efficient conversion of aquaculture inputs to fish weight gain, and significantly reduces farming costs.
Key Components
- Probiotic Preparation: Rich in beneficial bacterial strains like Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria. Optimizes the intestinal microenvironment to significantly enhance feed conversion rates and promote efficient nutrient absorption.
- Amino Acid & Protein Enhancer: Scientifically formulated with essential amino acids like lysine and methionine to precisely meet fish protein synthesis requirements. Accelerates muscle growth while effectively improving fish meat flavor and quality.
- Composite Vitamin-Mineral Premix: Comprehensively covers core nutrients including Vitamins A, D, E, calcium, phosphorus, and zinc, providing essential nutritional support for all growth stages and ensuring healthy development.
Mechanism of Action
Healthy fish intestines harbor a stable micro-ecosystem dominated by beneficial bacteria, whose metabolic products supply nutrients like vitamins and enzymes. Fish growth promoter is formulated with scientifically balanced plant powders, trace elements, and complex vitamins, combined with multiple beneficial bacteria through a specialized fermentation process.
Upon entering the fish gut, the beneficial bacteria rapidly colonize and multiply, suppressing harmful bacteria growth and maintaining gut microbial balance. Simultaneously, they release bioactive substances that enhance nutrient absorption, achieving the dual objectives of “rapid growth + healthy survival.”
Proper Usage Methods
- Routine Aquaculture: Add at 2% of feed weight for long-term mixed feeding, suitable for fish in normal growth stages.
- Special Circumstances: When fish exhibit stress reactions (e.g., agitation after water changes, reduced feeding), diarrhea, or respiratory diseases, add at 4% of feed weight for 3-5 consecutive days to rapidly restore health.
Optimizing Stocking Density and Fry Quality
Ideal Stocking Density
For Gambia ponds (water depth 1.5–2 meters), stock 3–5 tilapia per square meter and 2–3 catfish per square meter. Overstocking degrades water quality, intensifies feed competition, and slows growth; understocking wastes space and reduces profitability.
Selecting High-Quality Fry
- Source: Prioritize purchasing fry from local, reputable hatcheries to ensure pure strains and disease/injury-free stock.
- Quality Assessment: High-quality fry exhibit uniform body shape, vibrant coloration, active swimming behavior, and responsive reactions to external stimuli. They should be free of deformities (e.g., curved bodies, missing fins).
Pre-Stocking Preparations for Fry
- Quarantine: Place fry in a holding tank for 3-5 days to observe for disease symptoms, preventing pathogen introduction into the main pond.
- Acclimatization: Adjust the holding tank water temperature to match the main pond (temperature difference ≤2°C). Gradually add water from the main pond to reduce stress.
Disease Prevention and Fish Health Management
Common Fish Diseases in Gambia
- Bacterial Diseases: Conditions like fin rot and enteritis often arise from deteriorating water quality or spoiled feed. Affected fish exhibit rotting fin rays, inflamed red anuses, and abnormal fecal consistency/color.
- Parasitic Infections: Ichthyophthirius (white spot disease) and Trichodina infections are common. Infected fish develop white, dot-like cysts on their bodies, increased mucus secretion, and exhibit frantic swimming or frequent rubbing against pond walls due to discomfort.
- Fungal Diseases: Saprolegniasis often occurs during the fry stage or after fish injuries. Affected fish develop white, cottony fungal growths on their bodies, resembling a layer of fluff, severely impairing health and vitality.
Early Disease Recognition Signs
- Feeding abnormalities: Sudden reduction or cessation of feeding is the primary indicator.
- Behavioral changes: Frequent gasping at the surface, frantic swimming, clustering in pond corners, or solitary swimming away from the group.
- Physical abnormalities: Skin discoloration, hemorrhaging, fin rot, scale loss, or foreign objects attached to the body surface.
Natural Prevention Methods
- Precision water quality management: Establish a dynamic water quality monitoring system. Weekly test critical indicators like pH, ammonia nitrogen, and nitrite. Scientifically adjust water change frequency based on test data (recommended: replace 1/3 of water volume every 7-10 days). Maintain dissolved oxygen levels ≥5mg/L using aeration equipment to effectively suppress accumulation of harmful substances like ammonia nitrogen, fortifying the aquatic environment for healthy fish growth.
- Precision Feeding: Strictly enforce feed quality acceptance standards, eliminating moldy or expired feed. Supplement base feed with immune enhancers like yeast polysaccharides and vitamin C at appropriate ratios to boost disease resistance. Adopt the “small portions, multiple times, 80% full” feeding principle. Flexibly adjust feeding quantities based on fish size, water temperature, and feeding activity to prevent intestinal diseases caused by overfeeding.
- Ecological Environment Sanitization: Implement a “dual-track” disinfection system: Conduct routine monthly disinfection by broadcasting quicklime (20-30kg/mu) across the entire pond; Simultaneously, locally sourced natural herbal materials like neem leaves and rhubarb are boiled at a ratio of 5-10kg per mu and applied throughout the pond. This approach effectively eradicates pathogens while minimizing chemical residue, achieving green ecological disease control.
Basic Biosecurity Measures
- Tool Disinfection: Fishing nets, buckets, and other tools used across different ponds must be sun-dried or soaked in disinfectant before reuse to prevent cross-contamination.
- Prohibit Mixed Stocking: Do not introduce wild fish or fry of unknown origin into culture ponds to prevent pathogen introduction.
- Prompt Isolation: Immediately remove and isolate diseased fish to prevent spread. Dead or diseased fish must be buried deeply; do not discard them arbitrarily.
Conclusion
Successful fish farming in The Gambia hinges on “foundational safeguards and precise management.” By optimizing pond design and water quality, scientifically formulating feed, rationally controlling stocking density, and implementing disease prevention, rapid fish growth and enhanced farming profitability can be achieved without complex equipment or high investment. For local farmers, adhering to scientific farming practices while integrating local resources and sustainable principles will make aquaculture a stable pathway to prosperity.
- About Lima Biotech
- Careers-Lima Biotech
- Code of Conduct-Lima Biotech
- Conditions of Sale-Lima Biotech
- Contact-Lima Biotech
- Cookies Policy-Lima Biotech
- Find Agent-Lima Biotech
- Global Warehouses
- Investor Relations-Lima Biotech
- Legal Information-Lima Biotech
- Privacy Policy-Lima Biotech
- Success-Lima Biotech
- Sustainability-Lima Biotech
- World Class Manufacturing-Lima Biotech